in the Belt and Road Regions
| 2.1 | Elements of Religion |
| 2.2 | Features of Major Religions |
| 2.1 | Elements of Religion |
| Sacred Symbols | |
| Religious Beliefs | |
| Rituals | |
| Religious Communities |
 |
Profane and sacred
To some people, many objects in our daily lives provide us with opportunities to experience sacred encounters, for instance, when we see a stone, a bottle of water, a tree, an animal, or when we have supper. When a person experiences sacred encounters (pertaining to or connected with the divine) from a particular medium, the medium is reputed to be a form of "sacredness" and hence it becomes a sacred symbol. Symbol is sometimes a manifestation of the sacred
The sacred symbols make it possible for people to experience sacredness from the profane. Each religion has its own sacred symbols. Some abstract symbols are known as God, saint, prophet or spirit of superpower. For concrete symbols, to give two examples, the Cross is a representation of Jesus crucified and a talisman purchased from a temple represents a higher power's blessing for believers. |
 |
Religious beliefs are built on faith
Religious beliefs refer to people's faith in the sacred and the faith is often blended with devout attitude. People often seek for God's protection because they believe that the supernatural power would help them make a fortune and avoid disaster. Meaning of religious beliefs
Religious beliefs explain the meaning of life. They also provide directives for how we live in this world and in the afterlife. |
|
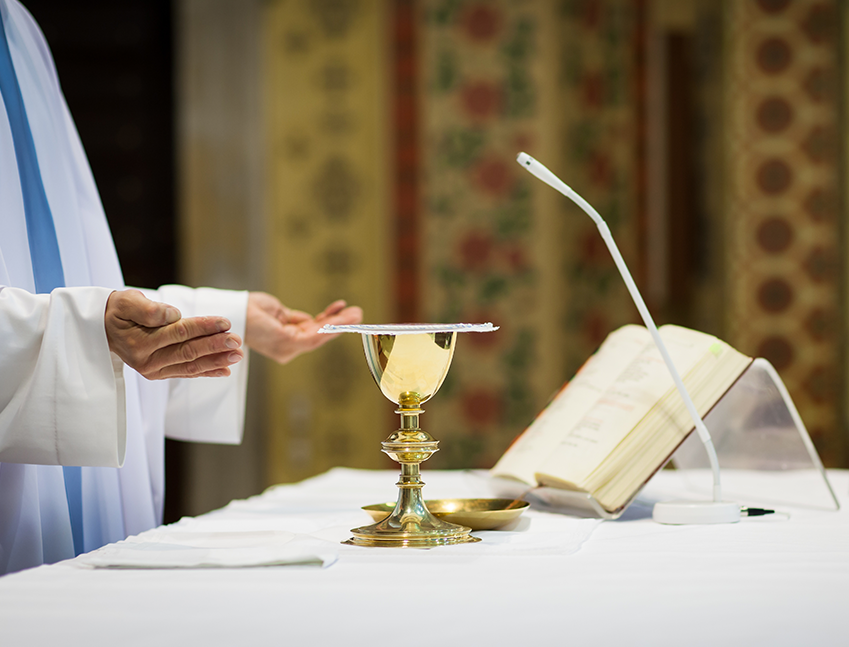
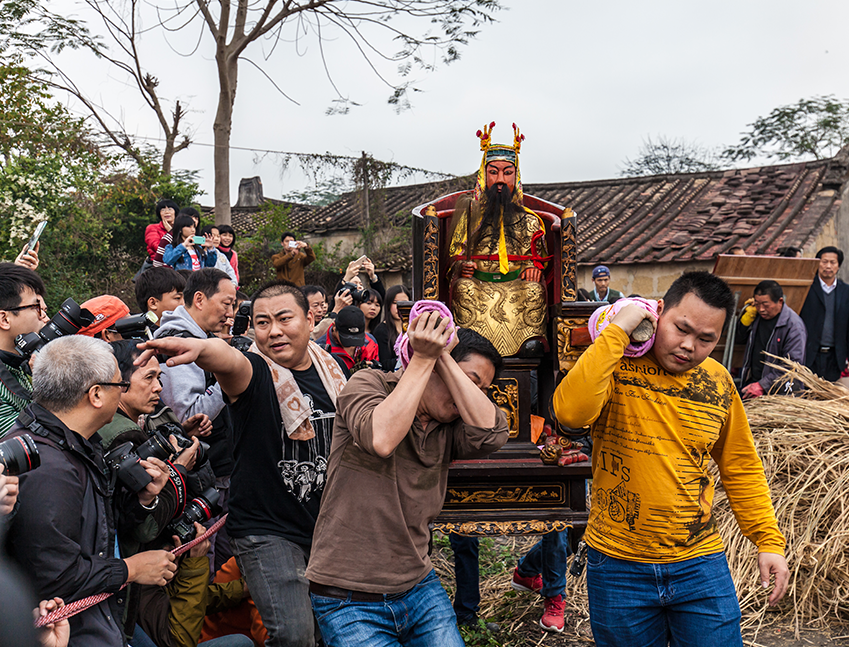
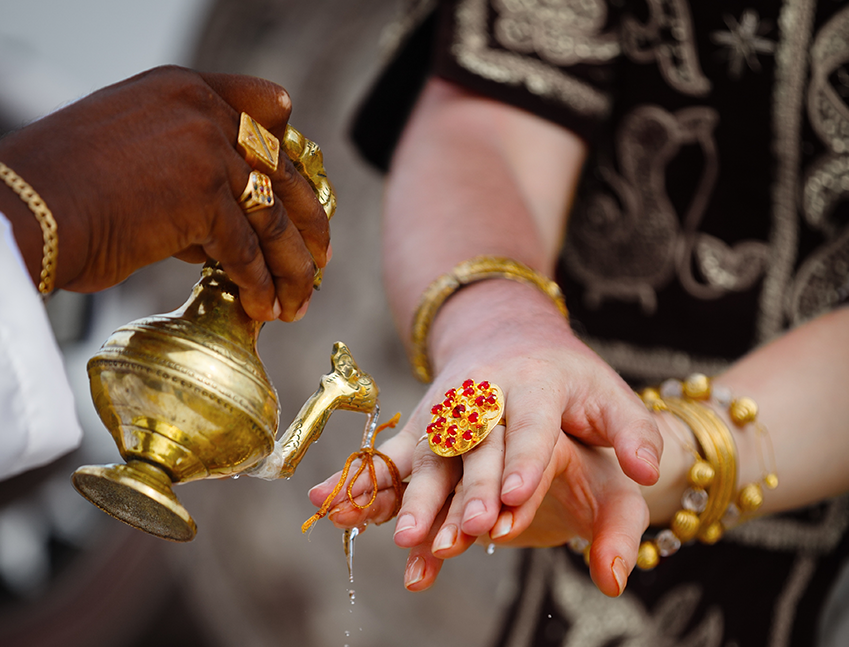
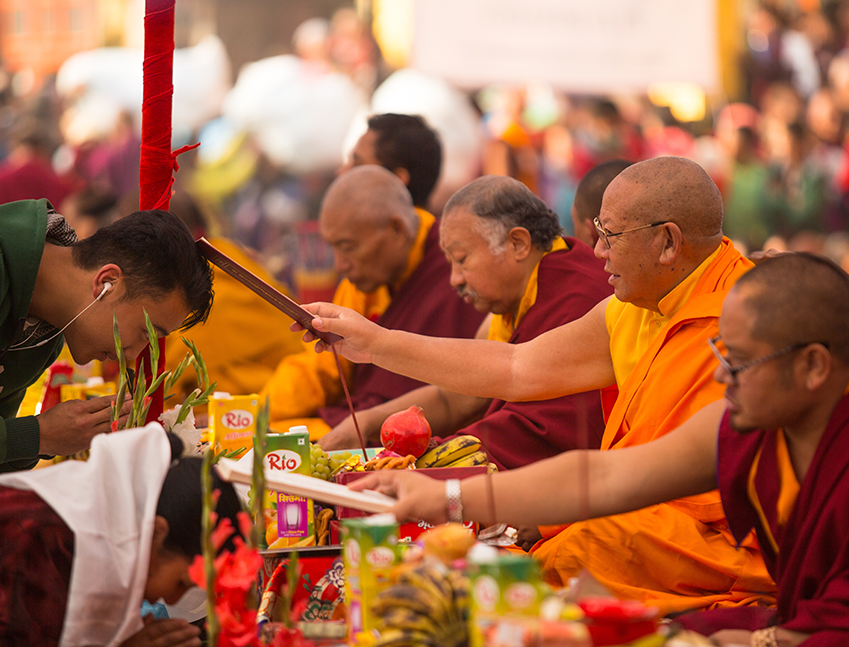
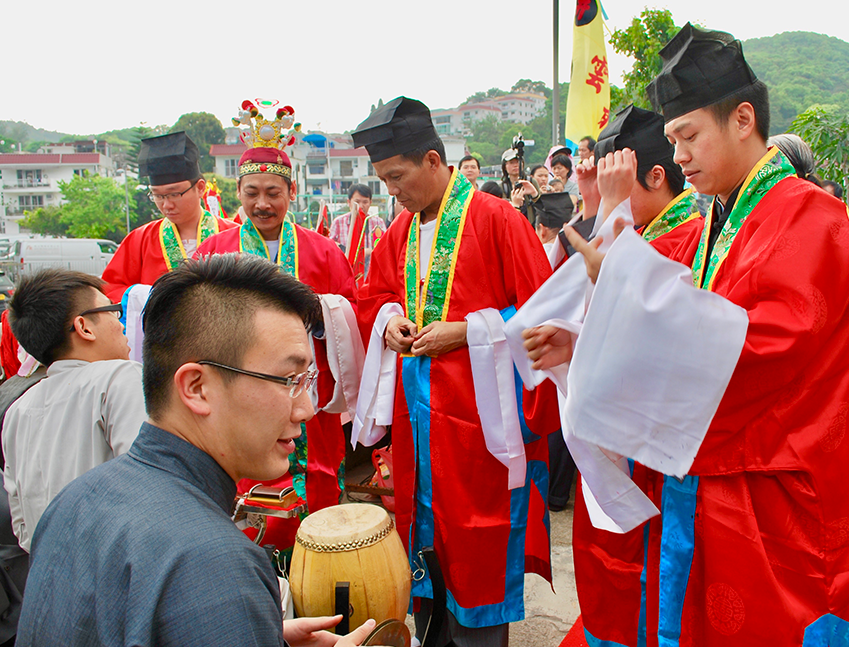
Religious rituals are activities with symbolic meaning.
Religious rituals are activities performed by specific priests at a specific time and in a specific place. Each ritual has its own unique significance within the religious tradition and allows participants to enter into the sacred world from the profane. Catholic Mass, Buddhist Fahui and Taoist Jiao are the most widely performed rituals in the world. |
 |
Religious communities maintain their religious beliefs.
Religious communities are gatherings of individuals who adopt common religion, habits, and practices. They adopt the teachings from a specific religious belief; for instance, some communities adopt vegetarianism as a practice of respecting sentient life. |

Dressing of Muslims

Dressing of Jews
| 2.2 | Features of Major Religions |


Do you know the missing features below? Click and answer them.
| Features of Christianity |
| Where did Christianity originate? |
| What is Christian building called? |
|
|
| Features of Christianity |
|

|

Cross as a representation of Jesus crucifixion for the whole human race. |

Do you know the missing features below? Click and answer them.
| Features of Islam |

Mosque
|
|
| Which one is an (are) Islamic ritual(s) / activity(ies)? |
| Features of Islam |
|

|

Crescent Moon and Star
One of the beliefs is that the Crescent moon represents the power of rebirth. The waxing and waning of the moon symbolizes the triumph over evil/adversity of Islam. |

Do you know the missing features below? Click and answer them.
| Features of Buddhism |
| What is the Buddhist place of worship called? |
| Which one is a Buddhist festival? |
|
|
| Features of Buddhism |
The Buddhist Canon (Dàzàngjīng) refers to the total body of Buddhist literature. Scriptures that known to people are: Hṛdayasūtra, Prajñāpāramitā- sūtra etc.
|

|

The dharmachakra (Wheel of the Dharma)
Turning the profane to sacred, smashing all the worries of mankind. The consummate wheel symbolizes the unobstructed Buddhist teachings. |
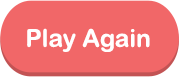
Understand the Features of Hinduism

India
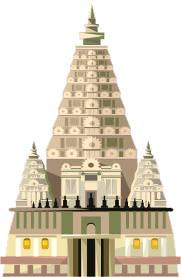
Hindu temple
There are over 120 Hindu religious festivals. Most of the festivals may be observed as acts of worship and offerings to deities, such as the Great Night of Shiva.
There are over 600 dialects in Hindu, the religious phrases vary greatly in different locations, such as Oum, Aum, Ovā Ovā Ovā Um, etc.
|
|
|
|

There are a wide variety of Gods in Hinduism. Gods they commonly worshiped are:
|

Sanskrit : Aum or Om
(a sacred sound in Hinduism) The connotations of "Om" vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions. One of the symbolic meanings refers to the eternal of the universe. |

Understand the Feature of Judaism

Israel

Synagogue
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

Star of David
It symbolizes pure new life. Some scholars say that it symbolizes the connection of God, Torah and Israel. |

Understand the Feature of Taoism

China
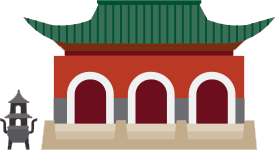
Taoist Temple
(Gong, Guan or Miao)
|
|
Taoist rituals can be classified as zhai (rituals for rescuing dead souls) and jiao (rituals of cosmic renewal), such as:
|
|
The Taoist Canon (Daozang) refers to the total body of Taoist literature, which includes: Nanhua Zhenjing (《南華真經》), Baopuzi (《抱朴子》) etc.
|
 There are many gods in Taoism, such as:
|

Taiji
It symbolizes all things are created by Qi (vital energy) from which Yin and Yang originate. |
- Indicate which festival(s) is/are related to religions in Hong Kong? What kind of activities are held to celebrate this/these festival(s)? How is the religious atmosphere during the festival?
- Compare two or more religious traditions by using one of the religious elements mentioned above. What are the unique features of these religions? (Hint: its local contents, history of the religion)
We could understand the religious traditions and the landscapes of humanities with reference to the different religious elements (sacred symbols, beliefs, rituals, religious communities, etc.) in the regions.
 HOME
HOME